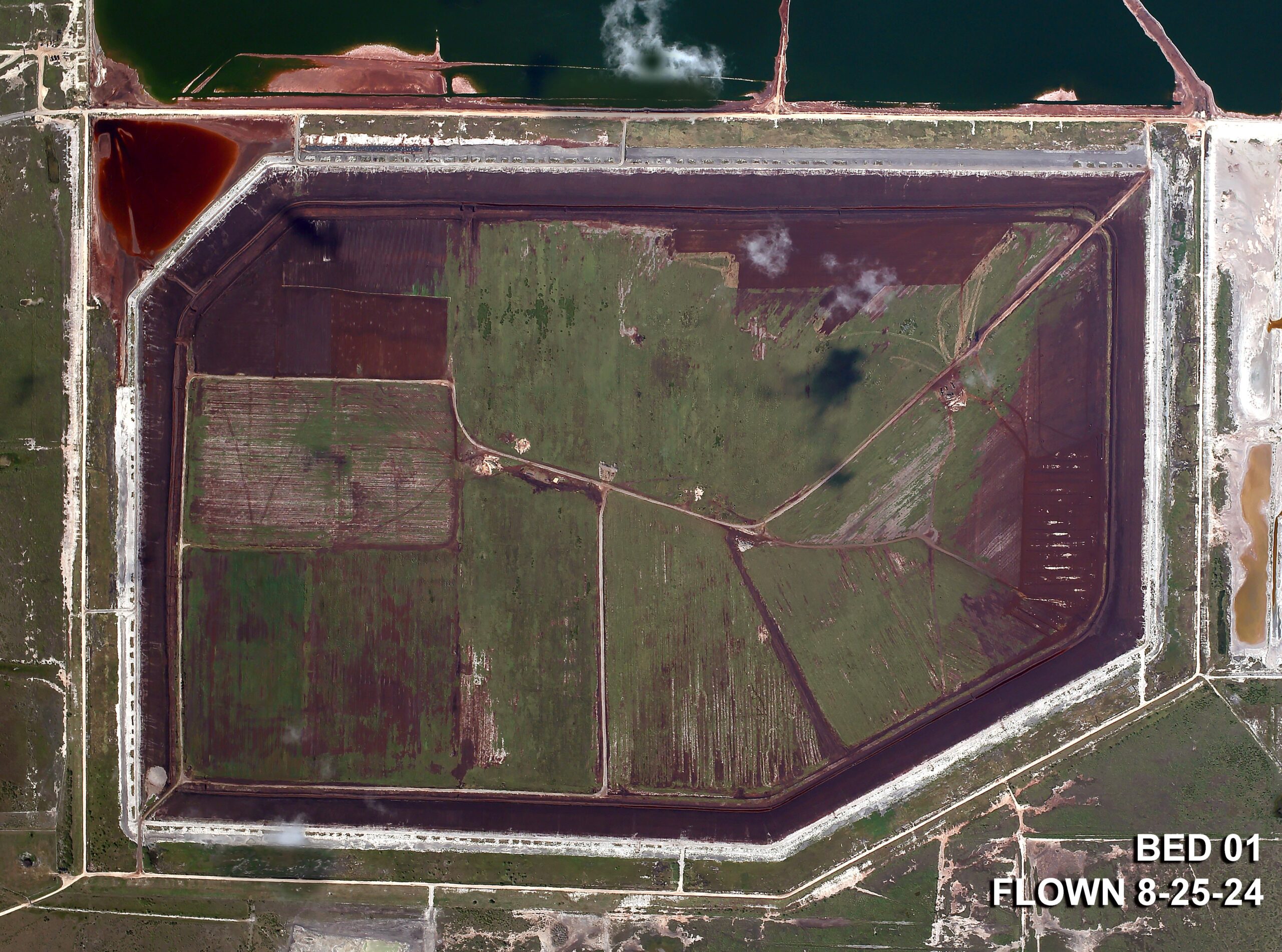
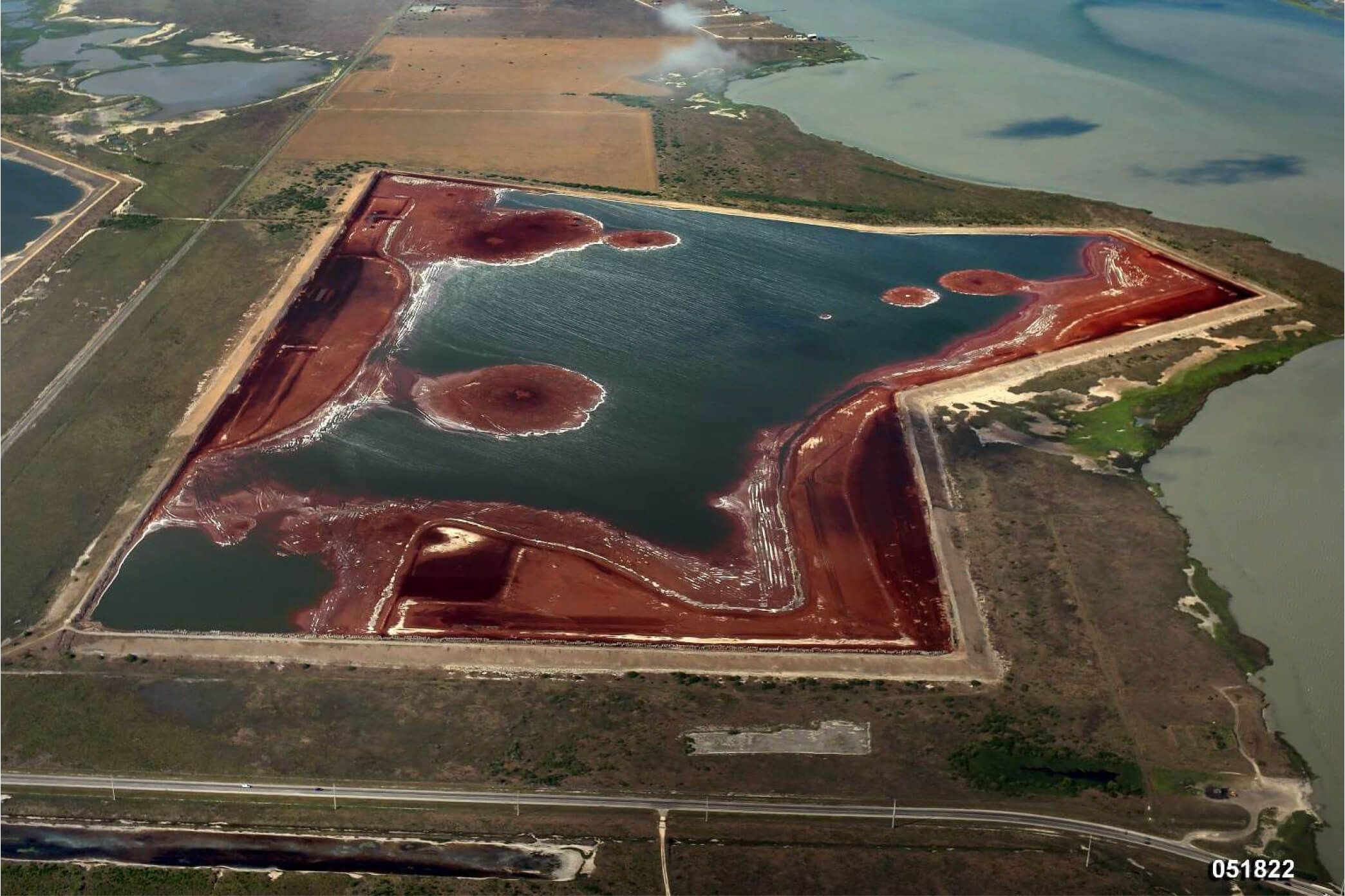
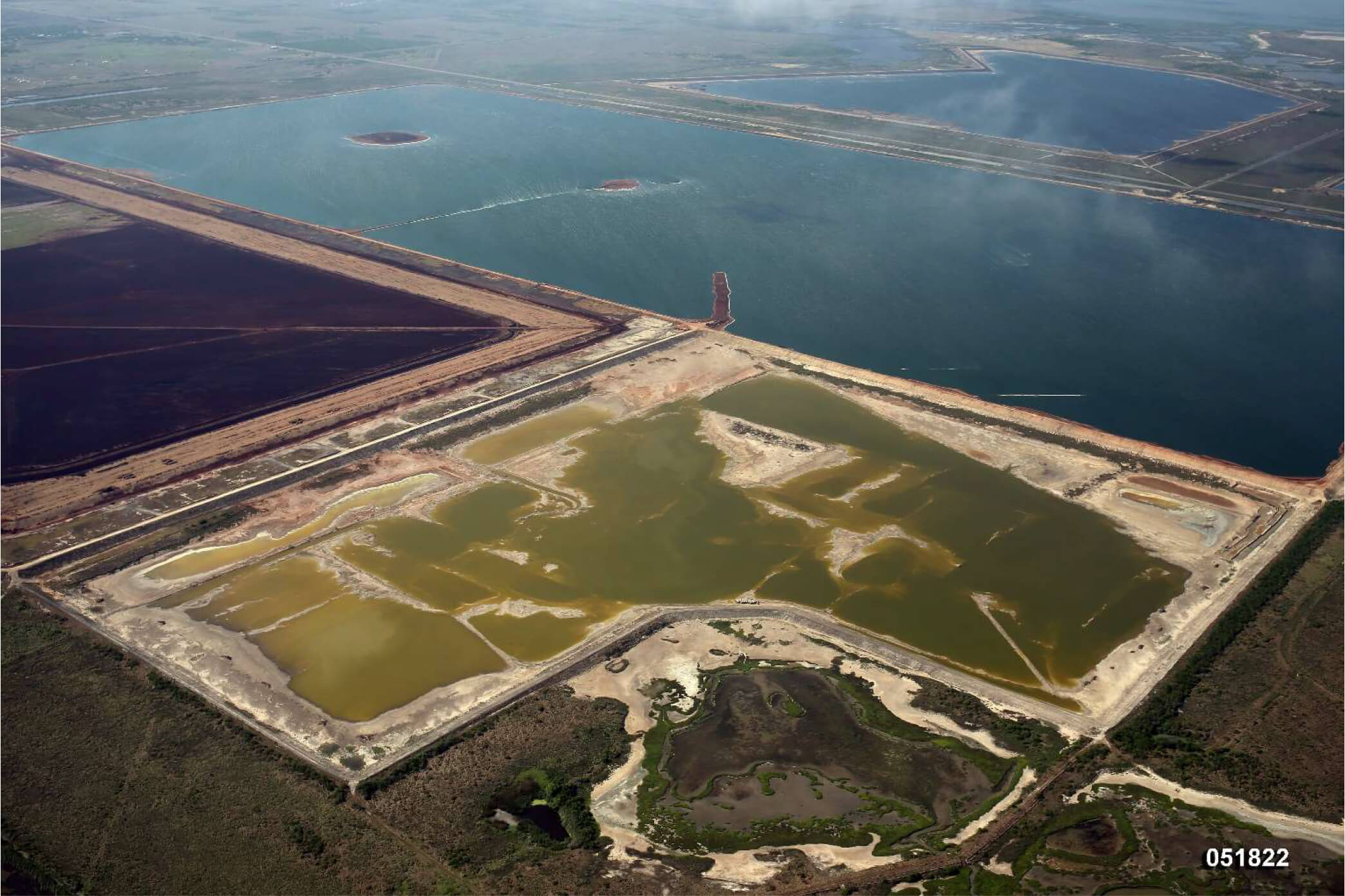
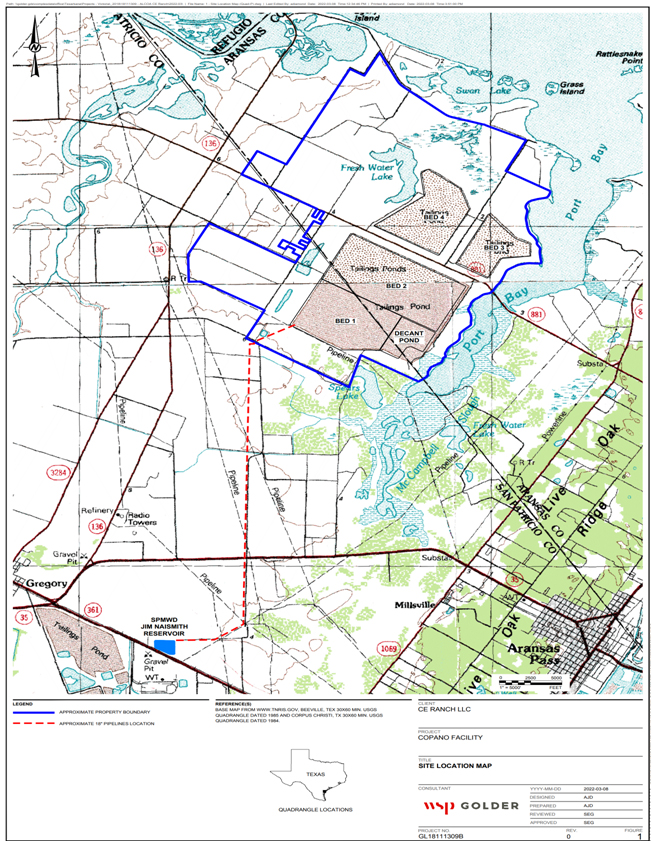
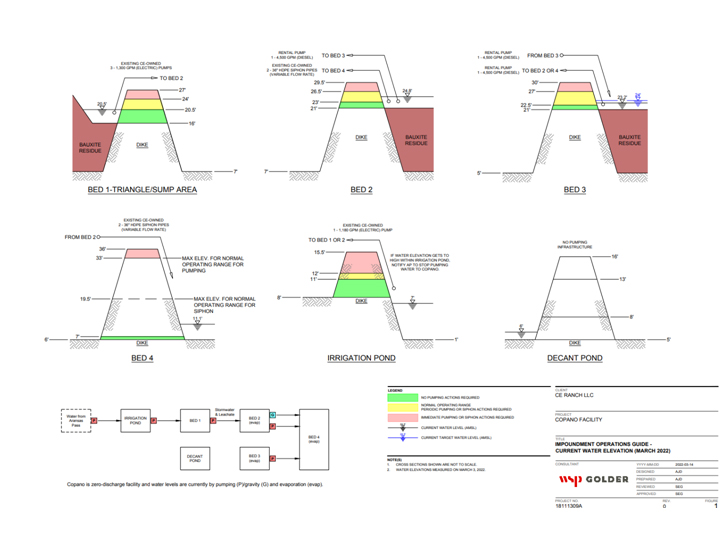
Foam Control
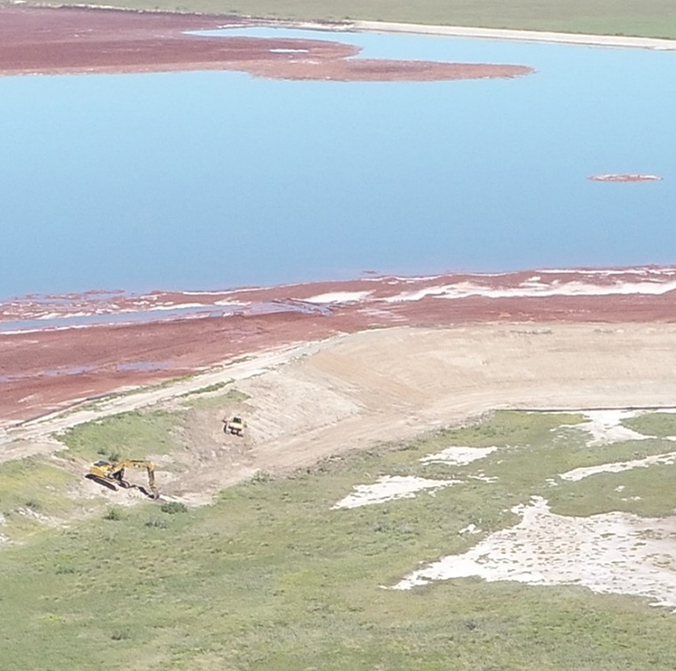
Foaming events can occur as organic matter decays within impounded surface water. Since 2018, CE Ranch has conducted successful foam control actions including managing impoundment water levels, installing barriers and applying anti-foaming agents.Admittedly those actions do not eliminate conditions that create foam, but rather minimize the potential for foam to leave the Copano property.